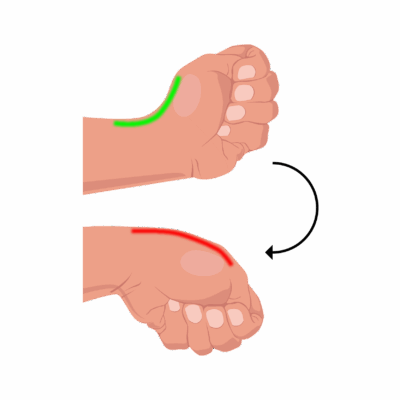
Finkelstein’s Test
Finkelstein’s Test is a provocative clinical maneuver used to diagnose de Quervain’s tenosynovitis—a painful inflammatory condition affecting the abductor pollicis longus (APL) and extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) tendons at the radial (thumb) side of the wrist. It helps distinguish de Quervain’s from other causes of wrist and thumb pain.
How the Test is Performed
-
Client position: Seated, with hand supported.
-
The client makes a fist with the thumb tucked inside the fingers.
-
The therapist (or client) gently ulnar deviates the wrist (bends wrist toward the little finger) while maintaining the thumb tucked—this stretches the involved tendons.
-
A positive test: Sharp, localized pain at the radial styloid (base of thumb/wrist, over APL and EPB) during the maneuver.
Clinical Significance
-
Positive Finkelstein’s Test is highly suggestive of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis.
-
The test is more specific and less likely than Eichhoff’s maneuver to cause false positives in normal wrists.
-
It differentiates de Quervain’s from osteoarthritis of the first carpometacarpal joint, scaphoid pathology, and other radial wrist pain sources.
Assessment
-
Use this test for clients with pain/swelling over the thumb side of the wrist, aggravated by thumb movement, gripping, or lifting.
-
Document when pain occurs, its localization, and any functional limitations for clinical records and interprofessional referrals.
Treatment
-
If positive:
-
Avoid deep, repetitive, or direct friction massage over the radial styloid and first dorsal compartment tendons (APL, EPB) to prevent aggravating inflammation.
-
Focus on gentle soft tissue release for the forearm and thumb extensors, myofascial approaches for compensating wrist and hand muscles, and pain-modifying techniques.
-
Educate clients about ergonomic changes (avoid repetitive thumb abduction/extension), activity pacing, and rest periods to reduce strain on involved tendons.
-
-
Suggest home care: gentle stretching, tendon gliding, ice, and protective splinting in acute stages.
Safety and Referral
-
Refer if there is persistent, severe, or function-limiting pain, swelling, or for diagnostic confirmation or corticosteroid injection or splinting.
-
Advise caution with activities that involve forceful or repetitive thumb movements and lifting.